How Do Search Engines Work?
There’s no doubt that most of us know what a search engine is, in its basic form: you type a few words into the platform and bam: you get your answers. But the internet is a big place and there are literally billions of different sites and forms of content out there that can act as a ‘solution’ to your ‘biggest problem’, so how do these search engines match up queries and websites with such accuracy?
Ultimately, there are ways you can make your website more appealing so that YOU are the one being served up to these users’ questions. And that’s called implementing search engine optimisation (SEO). Once you nail it down, you’ll reap more traffic, more engagement and better conversions – so how do you jump on board this opportunity?
The history of the search engine
Today, we have highly powerful search engines with Google at the very top of the pile. But it all started back in 1990 when the internet was at its embryonic stage in terms of public and commercial use. A search engine called Archie has been credited as the first of its kind. It was a tool for indexing FTP archives in a directory, a primitive but effective first step towards modern-day search engines like Google.
For some time, these search engines remained directory listings and Yahoo! emerged as the best of the lot after starting as a humble list of favourite web pages. Through time and popularity, it eventually grew into a searchable index directory and for a long period during the 1990s, it was an effective enough tool for a still-developing world wide web.
But simple directories would quickly become outdated as the Google searching engine started work on its algorithm, which has now dominated the market today.
Google first appeared on the scene in 1996 as a viable competitor for Yahoo! and offered a point of difference by ranking it search results by crawling and indexing in order of citation notation – the earliest form of following links (otherwise known as ‘backlinking‘). When one site mentioned another site, that site would receive a ‘vote’ in the Google rankings.
That would form the basis for the powerful and evolving engines that we now see today, like Google – which uses web crawling and indexing. It also employs artificial intelligence and a range of other features – including Google maps, images, news and much more. It left the other search engines – including Yahoo! – in the dust and today, it has over 90 per cent of the market share and remains on the cutting edge of innovation.
How do Google search engine algorithms work?
When you boil it all down, search engines are extremely simple beasts and only really have three basic functions: crawling, indexing and ranking. While these web crawlers and their capabilities were essentially developed by Google, its competitors have all adopted similar methodology to try and keep up with the algorithms that the main search engine now use across the board.
Here is how those three functions work:
Web crawlers and the nifty index
This is how search engines scour the web for content, finding the most relevant web page and code to bring them back to base (the user). A team of digital robots -called crawlers or spiders – are sent out to search for content on a regular basis – and they have a special appetite for new and updated text. There are many forms of content out there; including articles, videos, web pages, images. But for it to all be discoverable in search results, they all need links that connect them together through relevancy. This is why search engines crawl the internet to find all of these relationships and apply the sentiment to the web pages they crawl. From there, search engines work out how to prioritise (rank) one site over another – all through relevancy.
Indexing
Once these crawlers find these content pieces and links, they are stored in an index – a giant database of all of these links just waiting to be discovered. It is essential for a website to be indexed by web crawlers in order to be in with a chance of appearing in search results for a wide range of queries. But where they appear in these search results all comes down to a whole plethora of factors (read below).
How Googles search engine ranks a web page
This is the part that is most important for you when you are building, hosting, maintaining and updating new pages and existing content for an index. You want all of your links to be found by crawlers and you want them to be recorded so that they can be found by people searching for relevant content. When people type their query into a search engine, it is going to look in its index for the most relevant and highest quality content matches to deliver as results. So the higher your website is ranked in that index, the higher you are going to appear in searches and the more traffic you are going to get coming to your website. The answer: be as relevant and as value-driven as possible.
Context in searches
Not every user gets the same results when they put the same term into a search engine for their particular needs. That is because search engines work on a number of contextual factors, like location, user search history, settings and more. These search engines use more advanced techniques by the day, making it more and more of a challenge to adapt to these fluctuations if you’re a brand trying to rank content in the index.
The levels of artificial intelligence in search engine algorithms are allowing them to deliver more personalised results to each individual user by using a range of contextual signals that go beyond a simple cluster of words put into a search query.
Why am I not showing up in searches?
If your website is not appearing in search results, then you’re already missing out on crucial traffic streams to your website, which is bad news. So what can you do to fix that? First of all, you need to look at all of the reasons why you’re not showing up when you need to most. That’s somewhat of a challenge, but can be done.
Your site is brand-new
It takes time for a new website to be crawled, so exercise patience. While it can take up to six months for a new website to be crawled by search engines, it can also take as little as four days. There are a few things you can do to expedite this process, like submitting your sitemap to Google Search Console, establish links to your site from reputable pages with a high domain authority, publish well-written content, blogs and articles, and create an RSS Feed to send another signal to Google that your site has something new to be looked at.
Your site is blocking search engine crawlers
This is a simple checkbox in content management systems like WordPress. Sometimes pages should be blocking the crawlers that search engines use, especially if the information is hyper-specific to only a small group of people. Otherwise, this box should always be unchecked to allow bots access to your site, its pages and links. Without this function, all the efforts you’re putting in won’t work.
Your site has poor navigation
If your site’s navigation is confusing and mismanaged, Google’s search crawlers won’t be able to understand it either. And that means visitors will struggle to flow through your entire website or understand your content, making conversions a mess to untangle. In the end, this is money down the drain. Make it easy to navigate your site with links that make sense and a clear sitemap that you can submit directly to Google for better search results and user experience.
Your site has been penalised by Google
If you have been using ‘blackhat’ tactics to climb those Google search rankings, you may be in the bad books. Search engines work through a whole bunch of technical functions, so there’s no hiding behind shady techniques – at least not for long. You will always be caught out. That includes copy and pasting someone else’s content, using low-quality backlinks or spamming keywords (among other things).
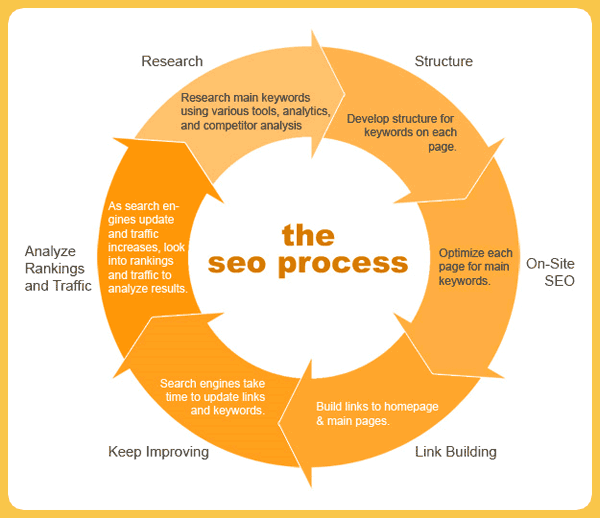
What is search engine optimisation and how can I use it?
The rankings in search engine results are not accidental. Google, Yahoo!, MSN, Bing (and the others) all have algorithms to determine which sites are the most relevant, have the best content and are going to deliver the best results to users. This is the universal language of how search engines work, no matter their differences. To make a website more attractive to engines, search results need to deem you as an authority and a provider of value. And that all starts with optimising your content and web pages through search engine optimisation (SEO).
There are many steps when it comes to successful SEO (please refer to our in-depth guides on how to achieve the best SEO strategies), but the basic first step centres around keywords. These are the words on your site that people are most likely to search into a search engine for answers around their question or needs.
For example, if you are a plumber in Tamworth, people are likely to find you using keywords and phrases like “best plumber Tamworth”, “cheapest plumber Tamworth” etc. It is essential to do research and discover how people are landing on your website in the first place so that you can utilise this behaviour in your SEO strategy and content. Doing this ensures you index for all the right phrases and a search engine continues to place you higher up i rankings.
What you need to optimise for search engines, content and index elements
- An optimised URL: that includes the right keywords. Using the previous example, www.tamworthplumbing.com.au would be an ideal fit
- Optimised images: Ensure your images (and video) include the right captions and alt text for search. This is a great place to include your keywords
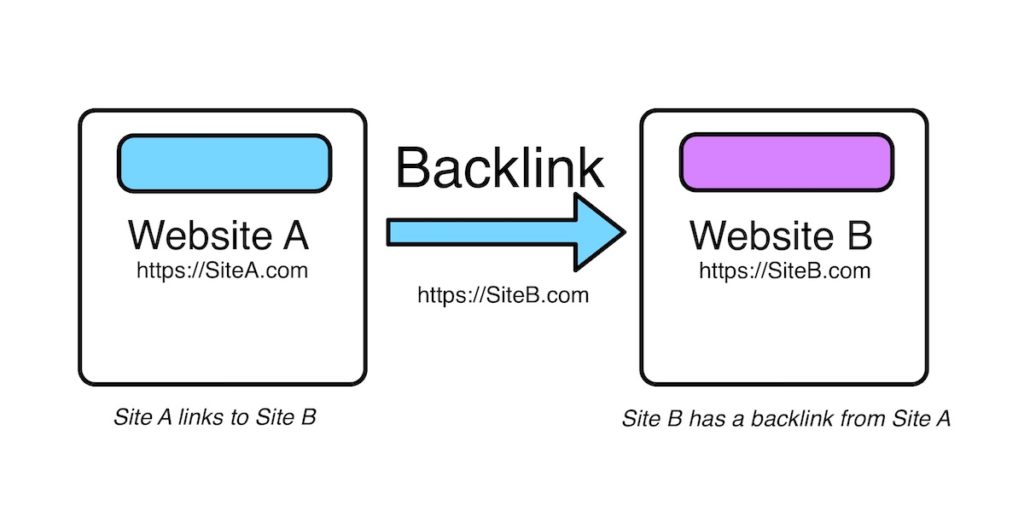
- Inbound links: Try to get as many reputable websites as possible to link back to your site, but make sure they are authoritative
- Internal links: Link to other pages on your website to make it an easier experience for visitors when they are navigating their way around your site
- Submit your sitemap to Google: As previously mentioned, search engines work by looking through your site; a sitemap helps rapid indexation
- Increase site speed: Google will favour websites that deliver a fast site speed experience
- Optimise your site for mobile: Most people are browsing on mobile devices these days and Google knows it
- Provide fresh content: Start a blog and write fresh, relevant and detailed content using your keywords. Search engines work magic for websites that regularly update and improve their content
How do I improve my rankings on a search engine?
There are tactics that some websites use to try and push their way up search engine rankings that violate Google’s standards and will lead to penalties. These tactics are called ‘black hat’ SEO strategies and you should never use them in a bid for a cheap and easy way to the top of the charts.
So what are black hat techniques? Like we said before, much of this has to do with keyword stuffing. This can be as blatant as blocks of text that include locations or phone numbers with no context or repeating keywords and phrases over and over to the point where they become annoying. Keyword stuffing can be a bit more subtle as well, with thin content that provides little or no value except to house keywords and phrases. In the end, all content must have value – always.

Cloaking is another negative tactic that involves showing one piece of content to users and a completely different piece to search crawlers. This is when websites are spamming users but showing the search bots “legitimate” content so they don’t get found out. Redirects are also frowned upon when users are funnelled from the URL they clicked on to a completely different site, especially when websites are hiding this activity from search crawlers.
Paid links can be a temptation but they are a trap. The only good backlinks are official ones that you’ve earned organically, and you want them to be from the most reputable sources possible. Services offering backlinks in return for financial remuneration are easily spotted by Google and you will be penalised as well.
So what is likely to come next when it comes to search engines? There are many schools of thought as to where the next evolution may come from in the world of search engine algorithms. Continued research and innovation surrounding artificial intelligence for search are likely to change the way we explore the web in the future. There have also been predictions that keyword search functions may become a thing of the past as search engines proactively deliver information to us before we even look for it; we are already seeing this through targeted advertising in search engines and social media platforms, for example.
Websites evolve every day and Google search is constantly refining its algorithm to deliver an improved search experience, but like Google blindsided Yahoo! back in the 1990s, it could be a new player on the scene that takes search engines to the next level in the very near future. Time will tell.





